Page 13 - Heartsafe | Better. Hands Down.
P. 13
HeartSafe-0000-FirstAidManual-Sept2016-R2.qxp_Layout 1 2016-09-28 2:04 PM Page 10
Introduction
Breathing
Breathing or respiration is the actual process where the body moves air into and out
of the lungs. Air contains 21% oxygen and very little carbon dioxide. Once the air
has passed through the airway and into the lungs, 1/4 of this oxygen gets consumed
by the body. Therefore, exhaled breath still contains 16% oxygen. It is for this reason
Artificial Respiration or rescue breathing has enough oxygen to help a person who
has stopped breathing.
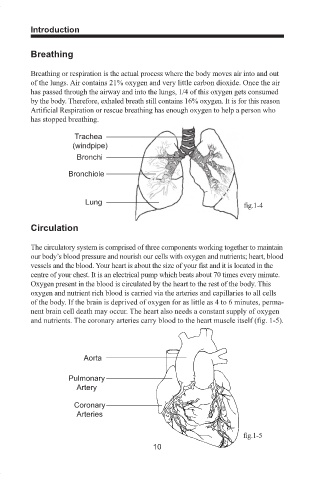
Trachea
(windpipe)
Bronchi
Bronchiole
Lung
fig.1-4
Circulation
The circulatory system is comprised of three components working together to maintain
our body’s blood pressure and nourish our cells with oxygen and nutrients; heart, blood
vessels and the blood. Your heart is about the size of your fist and it is located in the
centre of your chest. It is an electrical pump which beats about 70 times every minute.
Oxygen present in the blood is circulated by the heart to the rest of the body. This
oxygen and nutrient rich blood is carried via the arteries and capillaries to all cells
of the body. If the brain is deprived of oxygen for as little as 4 to 6 minutes, perma-
nent brain cell death may occur. The heart also needs a constant supply of oxygen
and nutrients. The coronary arteries carry blood to the heart muscle itself (fig. 1-5).
Aorta
Pulmonary
Artery
Coronary
Arteries
fig.1-5
10